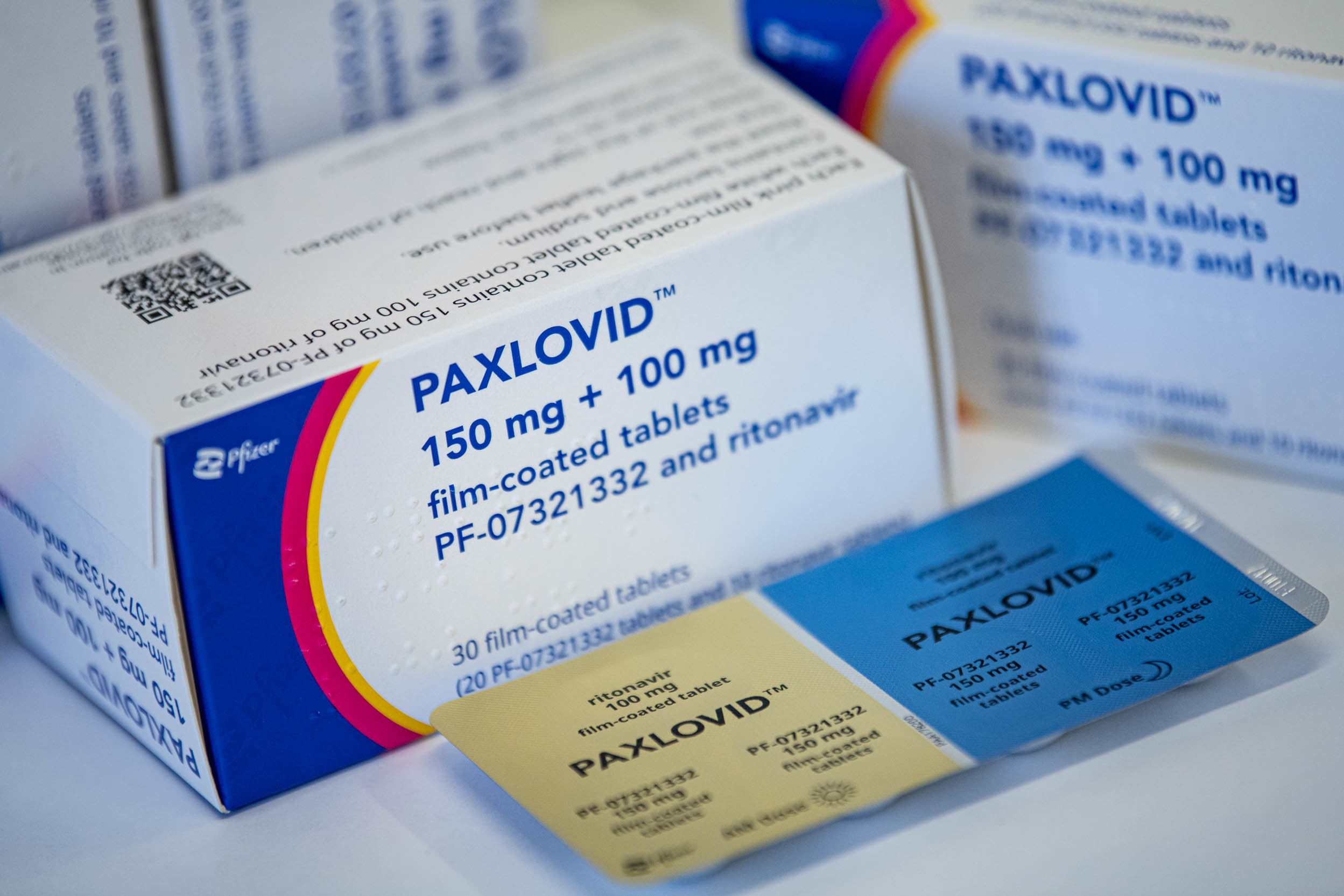
Buy PAXLOVID
What is Paxlovid?
Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir with ritonavir) is used to treat COVID-19, to help improve symptoms, and to lower the risk of becoming very sick. Paxlovid is an antiviral medication that works by stopping the virus from multiplying. It is used for mild to moderate COVID-19 patients who are more likely to progress to severe COVID-19.
You should start taking Paxlovid as soon as possible after diagnosis and within the first 5 days that you have had symptoms.
It contains two medications packaged together called nirmatrelvir (pink tablets) and ritonavir (white tablets). The usual Paxlovid dose is 2 nirmatrelvir tablets and 1 ritonavir tablet taken together twice daily for 5 days. The dose needs to be changed if you have kidney problems, and if you are taking certain medicines, Paxlovid is not suitable for some patients.
Paxlovid may be prescribed for an individual patient by physicians, advanced practice registered nurses, and physician assistants licensed or authorized under state law to prescribe drugs. It may also be prescribed for an individual patient by a state-licensed pharmacist under specific conditions.
Paxlovid side effects
Common Paxlovid side effects
Common Paxlovid side effects include a bad taste or change in taste, diarrhea, headache, vomiting, stomach pain, nausea, or high blood pressure.
Serious Paxlovid side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction (hives, difficulty breathing, swelling in your face or throat) or a severe skin reaction (fever, sore throat, burning eyes, skin pain, red or purple skin rash with blistering and peeling).
Call your doctor at once if you have:
- liver problems symptoms include loss of appetite, stomach pain (upper right side), tiredness, itching, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Ritonavir affects your immune system, which may cause certain side effects (even weeks or months after you’ve taken nirmatrelvir and ritonavir). Tell your doctor if you have:
- signs of a new infection–fever, night sweats, swollen glands, cold sores, cough, wheezing, diarrhea, weight loss;
- trouble speaking or swallowing, problems with balance or eye movement, weakness or prickly feeling; or
- swelling in your neck or throat (enlarged thyroid), menstrual changes, impotence.
This is not a complete list of side effects, and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Who can take Paxlovid?
Paxlovid can be used for mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients who are at high risk of severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. People who are at high-risk of severe COVID-19 are patients with:
- heart disease, diabetes, lung disease, cancer, blood disorders, immune disorders, mental health conditions, disabilities or other conditions
- being overweight or obese
- 50 years or older
- lifestyle factors, such as smoking
- physical, mental, and developmental disabilities.
Paxlovid is not suitable for everyone, and some patients will need to have dose modifications if they have certain medical conditions or take certain medicines.
Paxlovid is an FDA-approved medicine; it became FDA-approved on May 25, 2023, for adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients who are at high risk of severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death.
Paxlovid has Emergency Use Authorisation (EUA) to treat patients 12 to 18 years old for mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death.
Paxlovid is not approved for use as a pre-exposure or post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent COVID-19 or for the prevention of long COVID.
Warnings
It can interact with other medicines, causing severe or life-threatening side effects or death. It is important to know the medicines that should not be taken with Paxlovid. See the Interactions section below and check the interactions checker.
Paxlovid rebound and COVID-19 rebound
COVID-19 rebound is when COVID-19 symptoms return between 2 and 8 days after initial COVID-19 recovery, this can happen in some people that are in vaccinated, unvaccinated, Paxlovid treated and people who have not been treated with Paxlovid. When COVID-19 symptoms return in Paxlovid treated patients, some people have called it Paxlovid rebound.
The CDC states that “There is currently no evidence that additional treatment is needed with Paxlovid or other anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapies in cases where COVID-19 rebound is suspected.”
How does Paxlovid work?
It works as nirmatrelvir, is an antiviral medication that stops the virus from multiplying. Nirmatrelvir is a SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitor (also known as SARS-CoV2 3CL protease inhibitor) that works by inhibiting viral replication in the early stages of the disease to prevent progression to severe COVID-19.
Ritonavir is taken with nirmatrelvir to help slow the metabolism of nirmatrelvir so that it stays in the body for longer periods of time at higher concentrations to help combat the virus.
Before taking this medicine
You should not use Paxlovid if you are allergic to the active ingredients nirmatrelvir and ritonavir, or any of the inactive ingredients.
Some drugs have drug interactions with Paxlovid, and they should not be used with Paxlovid, such as those listed below.
- alfuzosin, colchicine;
- sildenafil (Revatio) when used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH);
- pain medicine – pethidine, piroxicam, propoxyphene;
- heart medicine – amiodarone, dronedarone, flecainide, propafenone, quinidine, ranolazine;
- antipsychotic medicine – lurasidone, pimozide, clozapine;
- ergot medicine – dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine;
- cholesterol-lowering medicine – lovastatin, simvastatin; or
- a sedative – riazolam, oral midazolam.
Paxlovid should not be started immediately after discontinuation of any of the following drugs:
- rifampin;
- St. John’s Wort;
- a cancer medicine – apalutamide; or
- seizure medicine – carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin.
Not all possible interactions are listed here. Also, see the Interactions section below and check the interactions checker.
Tell your doctor if:
- you have liver problems or a liver disease such as hepatitis;
- you have kidney problems;
- you have an HIV-1 infection;
- you are pregnant or breastfeeding, or
- you have any serious or chronic disease.
Pregnancy
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you are or if you become pregnant. It is not known if Paxlovid can harm your unborn baby. Ritonavir can make birth control pills or birth control skin patches less effective. Ask your doctor about other birth control options such as an injection, implant, vaginal ring, condom, diaphragm, cervical cap, or contraceptive sponge.
Breastfeeding
Tell your healthcare provider are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Paxlovid can pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with this medicine.
Be the first to review “PAXLOVID” Cancel reply
Related products
ORAL
ORAL
ORAL
ORAL
ORAL
ORAL





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.